What is TCS on foreign remittance?
If you’re ever in a place where you are planning to send money abroad, then you need to know about TCS – Tax Collected at Source. This is a key element of Indian tax regulations for money that is sent overseas. Here, income tax is collected directly from the remitting entity before funds go overseas. This IT regulation was mainly implemented to monitor the movement of money and tax these transactions. TCS on foreign remittance finds its basis in the Income Tax Act of 1961, along with other subsequent amendments.
2023 Budget and its changes in TCS rates
The Union Budget in 2023 brought about significant changes to the TCS rates, which were at 5%. Under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme, TCS was raised from 5% to 20%. The Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) enables you to make international transactions with ease.
How is TCS collected?
The TCS rate applies to all foreign remittance transactions, including international money transfers, buying overseas trip packages, investments, shopping and others. All personal fund transfers exceeding INR 7 lakhs are subject to 20% TCS, except it is not fully applicable to those remittances that are made for education or medical treatments.
Steps involved in TCS collection
Identifying the TCS Trigger: Banks and money transfer services check if your transaction needs TCS. This usually applies to sending large amounts (over ₹7 lakh).
Tax Collection: If TCS applies, the bank takes a portion of the money you’re sending (around 20%) as tax.
Receipt from Bank: The bank gives you a receipt showing the deducted TCS amount.
Tax Goes to Government: The bank deposits the collected TCS with the government.
TCS Report & Certificate: The bank files a TCS report with the government and may also provide you with a TCS certificate for your records.
The Latest Update on Taxation for Foreign Remittances
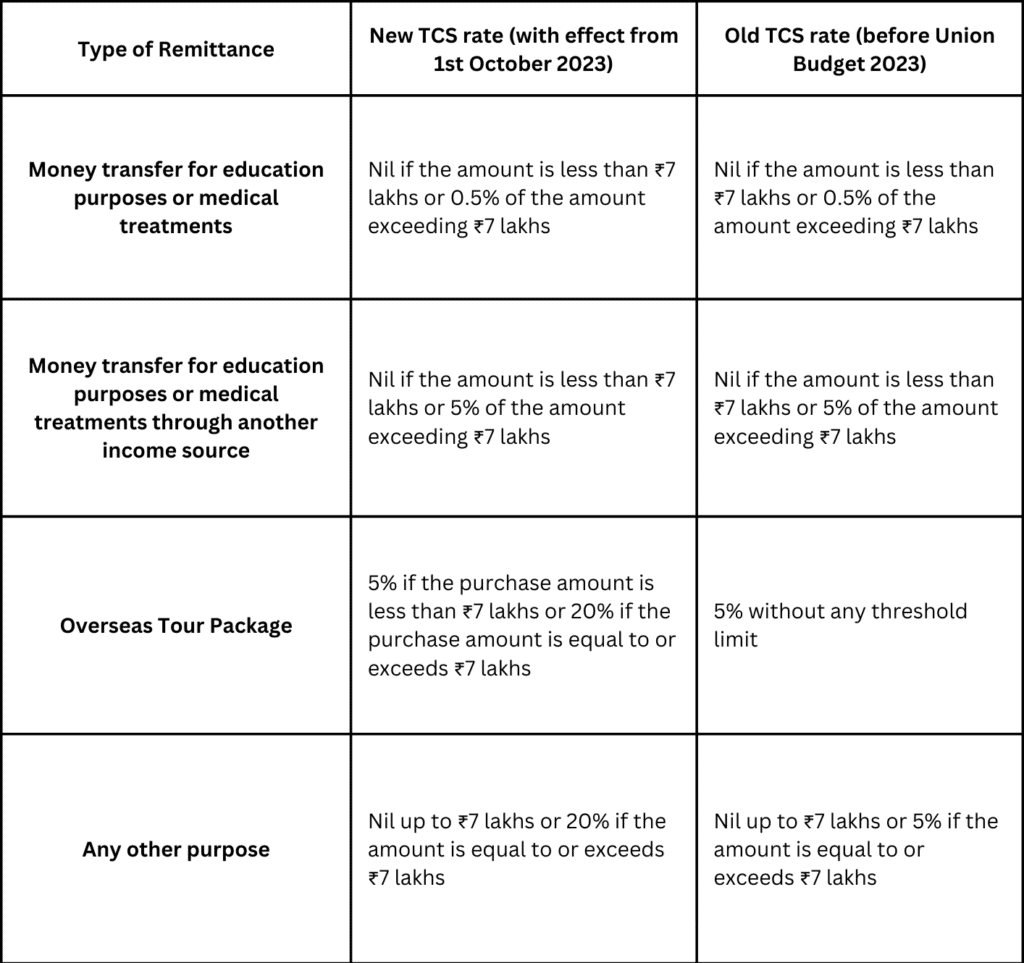
From 1st October 2023 onwards foreign remittances for Foreign equity investment under LRS and the purchase of overseas tour programs, the TCS rates saw an increase to 20%.
Let’s look at the table below, which shows the new and old foreign remittance TCS rates for different types of remittances:
Maximising Tax Benefits Through Tax Remittance under LRS
To get tax benefits from tax remittance on LRS, you should:
- Understand LRS Rules: Familiarise yourself with the LRS guidelines set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Know the permissible transactions. Stay updated on any changes or updates to the LRS rules to ensure compliance.
- Maintain Proper Documentation: Keep detailed records of all transactions conducted under the LRS. Preserve receipts, bank statements, and any other relevant documents related to remittances. Document foreign income sources, investment details, education expenses, and other financial activities abroad.
- Declare Foreign Income: If you have made any income from investments using LRS funds, declare it in your IT returns in India. This may include rental income from overseas properties, income from foreign investments etc.
- Claim Exemption: In cases where you have paid taxes on the income you earned, in the country in which you made it, you may be eligible for DTAA (Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement). This makes sure you don’t end up paying tax on the same income in both countries.
- Consult a Tax Advisor: Tax laws can seem confusing, especially when they involve foreign transactions. It is advisable to consult a professional who is knowledgeable in cross-border taxation. They can assist in personalised advice based on your financial circumstances.
- Effective Strategies for Avoiding the 20% TCS on Foreign Remittances
Is TCS on foreign remittances refundable?
Form 26AS displays TCS as a tax credit that can be utilised to offset the tax liability while filing an Income Tax Return (ITR). Additionally, TCS can also be adjusted against advance taxes at the time of filing. In cases where the TCS amount cannot be offset against the taxes payable or any other form, it will be eligible for a refund following the completion of the ITR filing (specifically, ITR-07).
It is important to note that the tax applies ONLY to the payer, not the recipient. The payer will get a TCS certificate and can claim a refund while filing the annual IT returns.
Who is eligible for a TCS refund?
If an individual has paid TCS on remittances, a refund can be pursued under specific conditions:
- If the total TCS amount exceeds the taxpayer’s annual tax liability.
- If the taxpayer files their Income Tax Return (ITR) on time.
- If the taxpayer possesses supporting documents like bank statements and Forex card statements.
How to Claim TCS while filing an ITR?
The 20% TCS incurred (on foreign remittances or other LRS-led expenses) can be claimed back when you file your Income Tax Return if you have paid more TCS than your actual tax liability. To claim the TCS refund, complete the ITR form’s relevant sections and provide supporting documentation. Consulting a tax professional or a qualified chartered accountant is advisable if you doubt claiming a TCS refund in your ITR.
While some argue that the 20% TCS is not an extra cost since you can eventually retrieve it, for some, the 20% charge may mean incurring a more significant upfront, blocking cash flow for immediate use.
Effective Strategies for Avoiding the 20% TCS on Foreign Remittances
To minimise the impact of increased TCS rates consider these strategies:
- Utilise Rs 7 Lakh Limit on International Cards: Payments under Rs 7 lakh on international debit or credit cards are TCS exempt. Make your reservations on international websites using these cards within the limit.
- Opt for Segregated Bookings: Book flights, accommodations, and sightseeing separately to avoid the 20% TCS. Buy flight tickets directly from airlines and hotels from official websites.
- Maximise Individual Limits: When travelling in a group, divide expenses so each person uses their Rs 7 lakh limit.
- Use an NRI Account: If you know a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) who has an NRI account, you might be able to transfer funds through them. Transfers from NRI accounts are exempt from TCS. (Note: This option depends on finding a willing NRI and may have tax implications for them, so consult a tax advisor)
- Education or Medical Treatment Purposes: Send money for education or medical treatment purposes. The 20% TCS won’t apply if the funds are being remitted for expenses or medical treatments. This is an option if you’re sending money abroad for yourself, your spouse, your children, or your parents’ education or healthcare needs.
Conclusion
In light of the 20% TCS impact on foreign remittances, addressing the concerns of international money senders becomes important. Understanding TCS regulations is essential for smooth transfers. By implementing the insights provided, understanding this tax burden is possible.The introduction of TCS aligns with the Indian Government’s drive for financial transparency and regulatory oversight. While the purpose is clear, its execution may pose challenges for cross-border financial activities.
If you’re unsure about how TCS applies to your situation, talking to a tax professional is a good idea. They can help you understand the rules and ensure your international money transfers go smoothly.
*Disclaimer:
The information contained herein is not intended to be a source of advice concerning the material presented, and the information contained in this article does not constitute investment advice. The ideas presented in the blog should not be used without first assessing your personal financial situation or without consulting a financial professional.